Backup & Restore GeoNode - Data Migration¶
The admin command to backup and restore GeoNode, allows to extract consistently the GeoNode and GeoServer data models in a serializable meta-format which is being interpreted later by the restore procedure in order to exactly rebuild the whole structure, accordingly to the current instance version (which may also be different from the starting one).
In particular the tool helps developers and amdins to correctly extract and serialize the following resources are on the storage and deserialize on the target GeoNode/GeoServer instance:
GeoNode (Resource Base Model):
- Layers (both raster and vectors)
- Maps
- Documents
- People with Credentials
- Permissions
- Associated Styles
- Static data and templates
GeoServer (Catalog):
- OWS Services configuration and limits
- Security model along with auth filters configuration, users and credentials
- Workspaces
- Stores (both DataStores and CoverageStores)
- Layers
- Styles
The tool exposes two GeoNode Management Commands, ‘backup’ and ‘restore’.
The commands allow to:
- Fully backup GeoNode data and fixtures on a zip archive
- Fully backup GeoServer configuration (physical datasets - tables, shapefiles, geotiffs)
- Fully restore GeoNode and GeoServer fixtures and catalog from the zip archive
- Migrate fixtures from old GeoNode models to the new one
The usage of those commands is quite easy and straight. It is possible to run the backup and restore commands from the GeoNode Admin panel also.
The first step is to ensure that everything is correctly configured and the requisites respected in order to successfully perform a backup and restore of GeoNode.
Warning
It is worth notice that this functionality requires the latest GeoServer Extension (2.9.x or greater) for GeoNode in order to correctly work.
Note
GeoServer full documentation is also available here GeoServer Docs
Requisites and Setup¶
Before running a GeoNode backup / restore, it is necessary to ensure everything is correctly configured and setup.
Settings¶
Accordingly to the admin needs, the file settings.ini must be tuned up a bit before running a backup / restore.
It can be found at geonode/base/management/commands/settings.ini and by default it contains the following properties:
[database]
pgdump = pg_dump
pgrestore = pg_restore
[geoserver]
datadir = /opt/gs_data_dir
dumpvectordata = yes
dumprasterdata = yes
[fixtures]
#NOTE: Order is important
apps = people,account,avatar.avatar,base.backup,base.license,base.topiccategory,base.region,base.resourcebase,base.contactrole,base.link,base.restrictioncodetype,base.spatialrepresentationtype,guardian.userobjectpermission,guardian.groupobjectpermission,layers.uploadsession,layers.style,layers.layer,layers.attribute,layers.layerfile,maps.map,maps.maplayer,maps.mapsnapshot,documents.document,taggit
dumps = people,accounts,avatars,backups,licenses,topiccategories,regions,resourcebases,contactroles,links,restrictioncodetypes,spatialrepresentationtypes,useropermissions,groupopermissions,uploadsessions,styles,layers,attributes,layerfiles,maps,maplayers,mapsnapshots,documents,tags
# Migrate from GN 2.0 to GN 2.4
#migrations = base.resourcebase,layers.layer,layers.attribute,maps.map,maps.maplayer
#manglers = gn20_to_24.ResourceBaseMangler,gn20_to_24.LayerMangler,gn20_to_24.LayerAttributesMangler,gn20_to_24.MapMangler,gn20_to_24.MapLayersMangler
# Migrate from GN 2.4 to GN 2.4
migrations = base.resourcebase,layers.layer,layers.attribute,maps.map,maps.maplayer
manglers = gn24_to_24.ResourceBaseMangler,gn24_to_24.LayerMangler,gn24_to_24.LayerAttributesMangler,gn24_to_24.DefaultMangler,gn24_to_24.MapLayersMangler
The settings.ini has few different sections that must carefully checked before running a backup / restore command.
Settings: [database] Section¶
[database]
pgdump = pg_dump
pgrestore = pg_restore
This section si quite simple. It contains only two (2) properties:
- pgdump; the path of the
pg_dumplocal command. - pgrestore; the path of the
pg_restorelocal command.
Warning
Those properties are ignored in case GeoNode is not configured to use a DataBase as backend (see settings.py and local_settings.py sections)
Note
Database connection settings (both for GeoNode and GeoServer) will be taken from settings.py and local_settings.py configuration files. Be sure they are correctly configured (on the target GeoNode instance too) and the DataBase server is accessible while executing a backup / restore command.
Settings: [geoserver] Section¶
[geoserver]
datadir = /opt/gs_data_dir
dumpvectordata = yes
dumprasterdata = yes
This section allows to enable / disable a full data backup / restore of GeoServer.
- datadir; the full path of GeoServer Data Dir, by default
/opt/gs_data_dir. The path must be accessible and fully writable by thegeonodeand / orhttpd serverusers when executing a backup / restore command. - dumpvectordata; a boolean allowing to disable dump of vectorial data from GeoServer (shapefiles or DB tables). If
false(orno) vectorial data won’t be stored / re-stored. - dumprasterdata; a boolean allowing to disable dump of raster data from GeoServer (geotiffs). If
false(orno) raster data won’t be stored / re-stored.
Warning
Enabling those options requires that the GeoServer Data Dir is accessible and fully writable by the geonode and / or httpd server users when executing a backup / restore command.
Settings: [fixtures] Section¶
[fixtures]
#NOTE: Order is important
apps = people,account,avatar.avatar,base.backup,base.license,base.topiccategory,base.region,base.resourcebase,base.contactrole,base.link,base.restrictioncodetype,base.spatialrepresentationtype,guardian.userobjectpermission,guardian.groupobjectpermission,layers.uploadsession,layers.style,layers.layer,layers.attribute,layers.layerfile,maps.map,maps.maplayer,maps.mapsnapshot,documents.document,taggit
dumps = people,accounts,avatars,backups,licenses,topiccategories,regions,resourcebases,contactroles,links,restrictioncodetypes,spatialrepresentationtypes,useropermissions,groupopermissions,uploadsessions,styles,layers,attributes,layerfiles,maps,maplayers,mapsnapshots,documents,tags
# Migrate from GN 2.0 to GN 2.4
#migrations = base.resourcebase,layers.layer,layers.attribute,maps.map,maps.maplayer
#manglers = gn20_to_24.ResourceBaseMangler,gn20_to_24.LayerMangler,gn20_to_24.LayerAttributesMangler,gn20_to_24.MapMangler,gn20_to_24.MapLayersMangler
# Migrate from GN 2.4 to GN 2.4
migrations = base.resourcebase,layers.layer,layers.attribute,maps.map,maps.maplayer
manglers = gn24_to_24.ResourceBaseMangler,gn24_to_24.LayerMangler,gn24_to_24.LayerAttributesMangler,gn24_to_24.DefaultMangler,gn24_to_24.MapLayersMangler
This section is the most complex one. Usually you don’t need to modify it. Only an expert user who knows Python and GeoNode model structure should modify this section.
What its properties mean:
- apps; this is an ordered list of GeoNode Object Models (or DJango apps). The backup / restore procedure will dump / restore the fixtures in a portable format.
- dumps; this is the list of
filesassociated to the DJango apps. The order must be the same of the property above. Each name represents thefile namewhere to dump / read the single app fixture. - migrations; some fixtures must be enriched or updated before restored on the target model. This section allows to associate specific manglers to the fixtures. Manglers are simple Python classes which simply converts some attributes to other formats.
- manglers; the Python mangler class to execute accorndingly to the fixture indicated by the migrations property. Manglers classes must be located into he geonode/base/management/commands/lib` folder.
Note
Manglers must be used when migrating from a GeoNode version to another one, i.e. where the original model differs from the target one. With the default distribution are provided manglers to convert from GeoNode 2.0 to GeoNode 2.4. Other versions may require other manglers or updates to the default ones.
Mangler Example¶
As specified on the section above, manglers are Python classes allowing developers to enrich / modify a fixture in order to fit the target GeoNode model.
The structure of a mangler is quite simple. Lets examine the ResourceBaseMangler of the gn_20_to_24 library, a mangler used to convert a GeoNode 2.0 Resource Base to a GeoNode 2.4 one.
class ResourceBaseMangler(DefaultMangler):
def default(self, obj):
# Let the base class default method raise the TypeError
return json.JSONEncoder.default(self, obj)
def decode(self, json_string):
"""
json_string is basicly string that you give to json.loads method
"""
default_obj = super(ResourceBaseMangler, self).decode(json_string)
# manipulate your object any way you want
# ....
upload_sessions = []
for obj in default_obj:
obj['pk'] = obj['pk'] + self.basepk
obj['fields']['featured'] = False
obj['fields']['rating'] = 0
obj['fields']['popular_count'] = 0
obj['fields']['share_count'] = 0
obj['fields']['is_published'] = True
obj['fields']['thumbnail_url'] = ''
if 'distribution_url' in obj['fields']:
if not obj['fields']['distribution_url'] is None and 'layers' in obj['fields']['distribution_url']:
obj['fields']['polymorphic_ctype'] = ["layers", "layer"]
try:
p = '(?P<protocol>http.*://)?(?P<host>[^:/ ]+).?(?P<port>[0-9]*)(?P<details_url>.*)'
m = re.search(p, obj['fields']['distribution_url'])
if 'http' in m.group('protocol'):
obj['fields']['detail_url'] = self.siteurl + m.group('details_url')
else:
obj['fields']['detail_url'] = self.siteurl + obj['fields']['distribution_url']
except:
obj['fields']['detail_url'] = obj['fields']['distribution_url']
else:
obj['fields']['polymorphic_ctype'] = ["maps", "map"]
try:
obj['fields'].pop("distribution_description", None)
except:
pass
try:
obj['fields'].pop("distribution_url", None)
except:
pass
try:
obj['fields'].pop("thumbnail", None)
except:
pass
upload_sessions.append(self.add_upload_session(obj['pk'], obj['fields']['owner']))
default_obj.extend(upload_sessions)
return default_obj
def add_upload_session(self, pk, owner):
obj = dict()
obj['pk'] = pk
obj['model'] = 'layers.uploadsession'
obj['fields'] = dict()
obj['fields']['user'] = owner
obj['fields']['traceback'] = None
obj['fields']['context'] = None
obj['fields']['error'] = None
obj['fields']['processed'] = True
obj['fields']['date'] = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S")
return obj
It extends the
DefaultMangler.The
DefaultMangleris a basic class implementing a JSONDecoderclass DefaultMangler(json.JSONDecoder): def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): self.basepk = kwargs.get('basepk', -1) self.owner = kwargs.get('owner', 'admin') self.datastore = kwargs.get('datastore', '') self.siteurl = kwargs.get('siteurl', '') super(DefaultMangler, self).__init__(*args) def default(self, obj): # Let the base class default method raise the TypeError return json.JSONEncoder.default(self, obj) def decode(self, json_string): """ json_string is basicly string that you give to json.loads method """ default_obj = super(DefaultMangler, self).decode(json_string) # manipulate your object any way you want # .... return default_obj
By default this mangler unmarshalls GeoNode Object Model from JSON and returns it to the management command.
The GeoNode Object Model can be modified while decoding by extending the
def decode(self, json_string)method.- json_string; actual parameter contains the JSON representation of the fixture.
- default_obj; is the Python object decoded from the JSON representation of the fixture.
It overrides the
def decode(self, json_string)method.The decoded Python object can be enriched / modified before returing it to the management command.
From Command Line¶
The following sections shows instructions on how to perform backup / restore from the command line by using the Admin Management Commands.
In order to obtain a basic user guide for the management command from the command line, just run
python manage.py backup --help python manage.py restore --help
--help will provide the list of available command line options with a brief description.
It is worth notice that both commands allows the following option
python manage.py backup --force / -f python manage.py restore --force / -f
Which will instruct the management command to not ask for confirmation from the user. It enables bascially a non-interactive mode.
Backup¶
In order to perform a backup just run the command:
python manage.py backup --backup-dir=<target_bk_folder_path>
The management command will automatically generate a .zip archive file on the target folder in case of success.
Restore¶
In order to perform a restore just run the command:
python manage.py restore --backup-file=<target_restore_file_path>
Restore requires the path of one .zip archive containing the backup fixtures.
Warning
The Restore will overwrite the whole target GeoNode / GeoServer users, catalog and database, so be very carefull.
From GeoNode Admin GUI¶
Login as
adminand click onAdminmenu option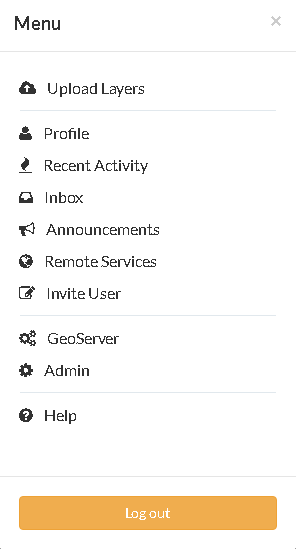
Look for
BackupsonBasesection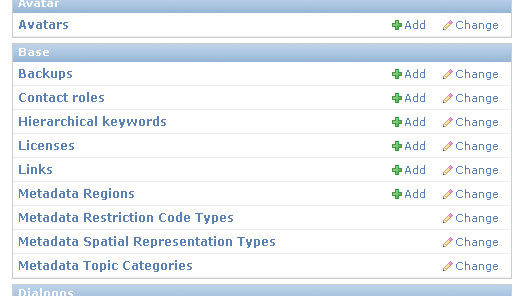
Add a new backup
Insert a
Nameand aDescription; also you must provide theBase folderwhere the backups will be stored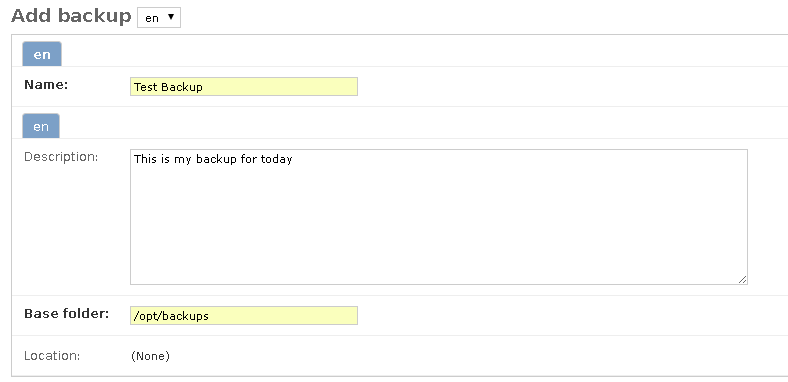
Warning
the
Base foldermust be fully writable from bothgeonodeandhttpd serversystem users.Click on
saveand go back to the Backups list main section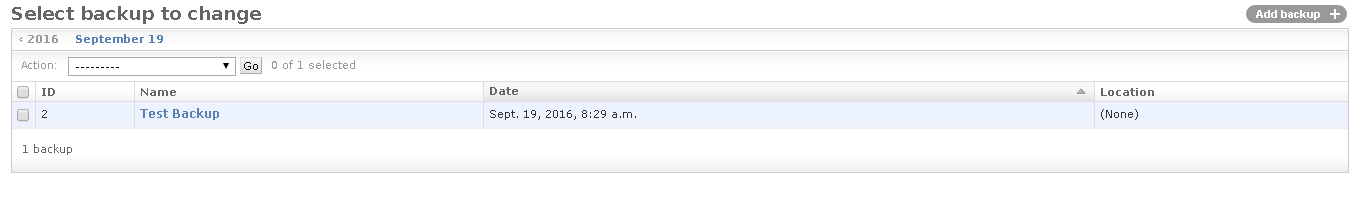
The new Backup is not ready until you perform the
Run Backupaction; in order to do that select the backup to run and from theActionmenu selectRun the Backup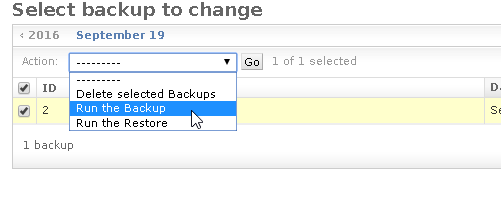
Note
A Backup is not ready until the
Locationattribute is filled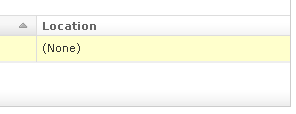
Click on
Yes, I'msureon the next section in order to perform the Backup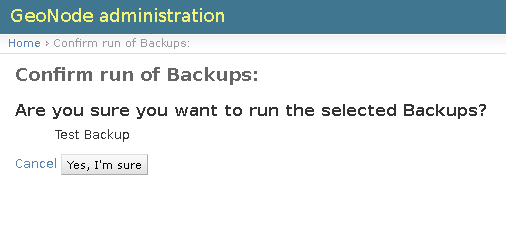
Note
The server page will wait for the Backup to finish (or fail).
The server page will wait for the Backup to finish (or fail); at the end of the Backup you will be redirected to the main list page.
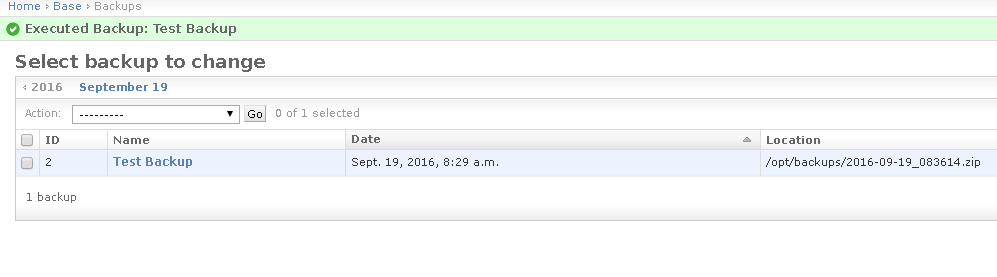
Note
At a successfull run, the
Locationattribute is filled with the full path of the backup archive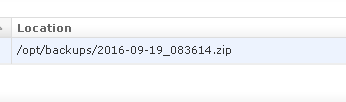
Warning
A Backup can always being updated later and / or executed again. The
Locationattribute will be updated accorndingly.Execute as many Backups as you want; they can all point to the same
Base Folder, the new backups will generate new unique archive files any time.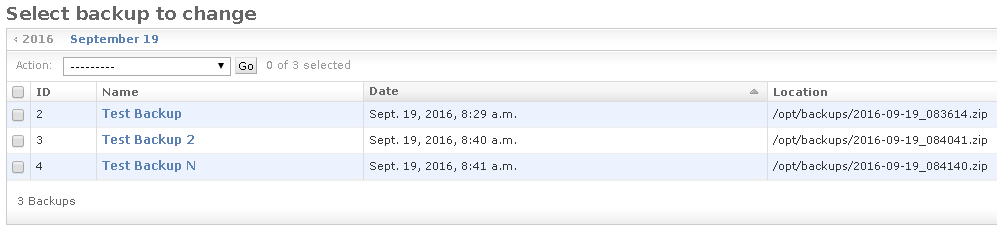
In order to Restore a zip archive, just select the instance to restore from the list and from the
Actionmenu lunch theRun the Restoreoption.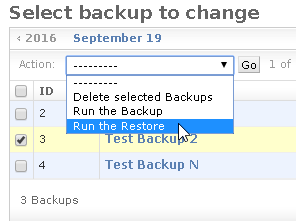
Click on
Yes, I'msureon the next section in order to perform the Backup
Note
The server page will wait for the Backup to finish (or fail).
Warning
The following target GeoNode folders must be fully writable from both geonode and httpd server system users
- geoserver_data_dir/data
- geonode / settings.MEDIA_ROOT
- geonode / settings.STATIC_ROOT
- geonode / settings.STATICFILES_DIRS
- geonode / settings.TEMPLATE_DIRS
- geonode / settings.LOCALE_PATHS
Warning
The Restore will overwrite the whole target GeoNode / GeoServer users, catalog and database, so be very carefull.